The American Psychological Association (APA) format is the most common style used to cite sources within the social sciences. This handout will give you a brief guide on the Publication Manual of the APA. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th Edition).

APA Citation Format Guide for Academic Papers
The American Psychological Association (APA) format is the most common style used to cite sources within the social sciences. Other most common academic citation styles are the Modern Language Association of America (MLA), Chicago/Turabian, and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The IEEE style is a numbered referencing style that uses citation numbers in the text of the manuscript, provided in square brackets. We will discuss the IEEE style in a separate work later. This article will give you a brief guide on the Publication Manual of the APA. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th Edition). Before discussing the APA format in detail, we will explain why academic referencing is of importance.

Academic referencing acknowledges and gives credit to the sources used by a scientific manuscript. It allows you to recognize other research and ideas used in your own study. Furthermore, academic referencing validates and strengthens your arguments. In the APA style, it is necessary to link the citations to the list of works cited in an academic manuscript.
Aside from giving due acknowledgement to other research works, academic referencing allows readers to be informed of the works cited in your study. Citing each source in your academic writing has implications. Academic referencing implicates to the readers that you are not the first and sole writer of a certain subject. Moreover, it allows your readers to examine how dated the information is and enables writers to realize that they are using others’ ideas in creating new approaches. Hence, this process gives readers the opportunity to track the references and get more ideas about a particular point made by the author.
As we discussed in our blog “The Importance of Academic Referencing and Citing,” sources must be cited whenever you use words, facts, ideas, or explanations from other works, even if you have not used their exact expression.
Of note, plagiarism is the act of using someone else’s work as if it was your own. The common examples of plagiarism are copying texts or ideas without referencing, incorrect referencing, and even paraphrasing sentences without referring to someone else’s original sentence structure. Thus, not citing your sources properly can be considered an act of plagiarism, which can possibly lead to a failed grade or loss of an academic position.
The APA format mainly consists of the following parts: in-text citation and reference list entry.
In-text citation (parenthetical citations): The APA format in-text citations are included in the sentence where the information is used. Such citations are presented after the quote or paraphrase taken from another work. In-text citations must contain the author(s)’ last name(s) and the year of publication only, for example, (Robinson, 2012) or (Acemoglu & Robinson, 2012). This format identifies and helps locate the full source in the reference list.
Reference list entry: Full publication details are listed alphabetically on the bibliography page, which appears right after the main text. The reference provides all the information that is essential to locate the sources.

An in-text citation (parenthetical citation) is an exact way to demonstrate to the readers where the original idea came from and to give credit to the original writer. It implicates to the readers that you are not the first writer who started the topic. Moreover, it allows your readers to understand how dated the information may be and enables writers to demonstrate that he/she is using others’ ideas to create a new idea. The APA format requires the inclusion of the last name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication in in-text citations. When you directly quote a source, it is also required to include the page number(s) (preceded by “p.”). Articles with one or two authors include all names in every text citation. Below are some useful examples of in-text citations:
According to a study… (Adam, 1992).
Direct quotation (Adam, 1992, pp. 223–227).
If the author's last name is stated in the sentence, always place the year in parentheses immediately after the name.
(Wan, 2001).
Wan's (2001) study reveals that ….
When you have two authors, you must separate their last names with an ampersand (&). When you have three or more authors, you must separate their last names using commas. The last two authors’ last names should be separated by both a comma and an ampersand (in a citation) or “and” (in the running text). Thus, use the word "and" between the authors’ last names within the text and use the ampersand in parentheses.

Below are some examples:
The research by Acemoglu and Robinson (2012) argues ….
(Acemoglu & Robinson, 2012).
Both authors’ last names should be separated by the word “and” if the names are included in the sentence. For the citations in parentheses, you need to use an ampersand (&), not “and.”
Acemoglu and Robinson (2012) claimed that political and economic institutions can promote economic growth.
Research indicates that political and economic institutions can promote economic growth (Acemoglu & Robinson, 2012).
Direct quotations:
“Nations fail today because their extractive economic institutions do not create the incentives needed for people to save, invest, and innovate” (Acemoglu & Robinson, 2012, p. 372).
Citing a source with three–five authors takes up a lot of space in the text. Thus, we need to shorten the references when we use the source for subsequent citations. In such a case, we use “et al.,” which means “and others.” Its usage is determined by the number of authors in a particular source and whether it is the first time a reference has been cited in your study. In this way, you do not have to write all authors’ last names. In the APA format, present all the authors’ last names for the first in-text citation, and then use “et al.” after the last name of the first author for subsequent citations.
First citation:
A recent study suggests that there is … (Aneshensel, Rutter, & Lachenbruch, 1991).
Aneshensel, Rutter, and Lachenbruch (1991) claimed that….
Subsequent citations:
In this study, several participants made use of … (Aneshensel et al., 1991).
Aneshensel et al. (1991) emphasized that ….
When you use six or more authors in your in-text citations, simply use only the first author’s last name followed by “et al.” and the year of publication for all in-text citations.
Davidson et al. (2001) stated that ….
(Davidson et al., 2001)
When the first author's last name and the years of publications are the same for more than one reference, include enough additional co-author names to eliminate ambiguity and use a comma after the last name.
(Davidson, Mark, et al., 2018).
(Davidson, John, et al., 2018).
When your source of reference is published by an organization instead of an individual, you must cite the institution’s name as the author. Type out the full organization name for the reference list.
First citation:
A newly released report reveals that… (American Psychological Association [APA], 2014).
Subsequent citations:
(APA, 2014).
In an APA citation for web pages, it's written in this order, in parentheses: (Year, Month Day). If the webpage names an individual author, cite their name first:
Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Date). Title of page. Site name. URL
If the online resource was written by a group or organization, use the name of the group/organization as the author. Besides, if the author and website name are the same, omit the website name from the citation:
Group name. (Year, Month Date). Title of page. Site name. URL
If the webpage's author is not listed, start with the title instead. Besides, add a retrieval date when the page's content is likely to change over time:
Title of page. (Year, Month Date). Site name. Retrieved Month Date, Year, from URL
Website in reference list should not be italicized.
If the citation is directly quoted from another source, you should place it between quotation marks.

To be more precise, page number(s) can be included in your citations (preceded by “p.” or “pp.”).
“Nations fail today because their extractive economic institutions do not create the incentives needed for people to save, invest, and innovate” (Acemoglu & Robinson, 2012, p. 372).
or
According to Acemoglu and Robinson (2012), “nations fail today because their extractive economic institutions do not create the incentives needed for people to save, invest, and innovate” (p. 372).
Multiple sources can be cited in one sentence by separating them using semicolons.
Several studies reveal that … (Aneshensel et al.,1991; Adams, 1992; Acemoglu & Robinson, 2012).
For studies published in the same year by the same author, add alphabetic designators to the year of publication in both the in-text citation and reference list.
(Wan, 2001a, 2001b).
For works published in different years by the same author, place the years of publication in a chronological sequence separated by commas.
(Wan, 2001, 2003).
An APA style reference list or bibliography includes a complete list of references used in your study, including the author(s) name(s), date of publication, and title, among other important information.
An APA style reference list must start on a new page at the end of the main text.
It must be alphabetically ordered by the name of the first author or by the title of the sources with no author.
If there are multiple studies by the same author, these are ordered by the year of publication; if the studies are in the same year, they are ordered alphabetically by the title and are allocated a letter (i.e., a, b, c) after the year of publication.
An APA style reference list must contain all the references used in the in-text citations.

Remember that the APA style reference format differs depending on the type of source. Here are some types of sources:
Article in a journal
Article in periodical
Book
Book section
Conference proceedings
Report
Website
Document from website
Sound recording
Patent
Case
Reference examples for books with the personal author(s):
General format:
Author’s Last Name, First Initial. Second Initial. (Year of publication). Title of the book. Place of Publication: Publishing Company.
Book by one author (book titles should be italicized):
Wan, T.H. (2002). Evidence-based health care management. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Book by two authors (book titles should be italicized):
Acemoglu, D., & Robinson, J. (2012). Why nations fail: The origins of power, prosperity, and poverty. New York: The Crown Publishing Group.
Article in a journal (journal names should be italicized):
Aneshensel, C.S., Rutter, C.M., & Lachenbruch, P.A. (1991). Social structure, stress, and mental health: Competing conceptual and analytic models. American Sociological Review. 56:166-178.
Website (nothing should be italicized)
DeCoster, J. (2020, January 6). Overview of factor analysis. Retrieved from http://www.stat-help.com/notes.html
There are some common formatting rules an author must adhere to when writing a scientific paper in the APA format. Here are some basic requirements:
The text in the APA format must be double spaced.
The margins of the document must be set to one inch (or 2.54 cm).
A left-aligned running head must be used with a shortened title on all pages.
It is strongly recommended to use Times New Roman in 12 pt. However, if this suggestion does not make sense for the purpose of your document, you should check with your target journal or institutions’ specific manual for the best approach for your document.
You should also check other requirements for the title page, running head, abstract, keywords, headings, and subheadings.
According to Cambridge University, submitting other’s work as part of a writer’s own without clearly recognizing the original author is considered plagiarism. In other words, plagiarism is an act of fraud because it comprises both stealing someone else's ideas and being dishonest about it subsequently. The Office of Research Integrity clearly emphasizes that plagiarism is a criminal offense and is considered both a theft or misappropriation of an intellectual property and the substantial unattributed textual copying of another's work.
The following tips may be helpful to avoid plagiarism:
It is one of the most challenging problems to handle, especially with the spread of the Internet, which has facilitated easier access to information. The best way to avoid copy-pasting is to adopt the act of “paraphrasing.” By paraphrasing, you reconstruct others’ ideas in your own sentences and provided a citation of the source.
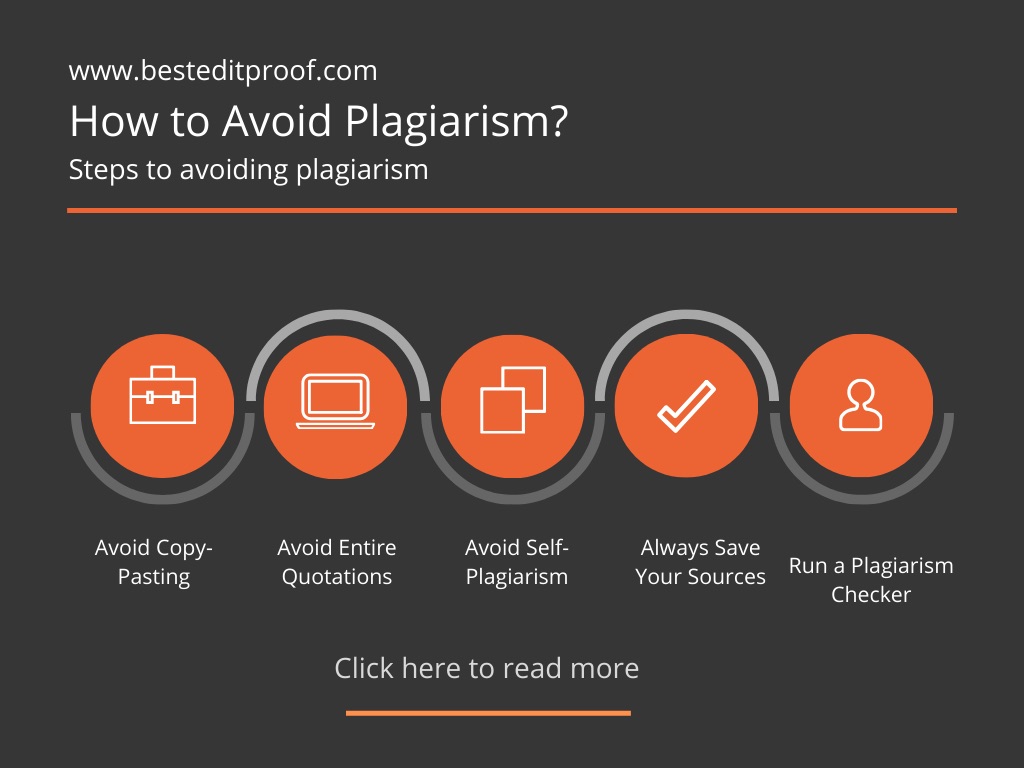
If you need to put the exact statement from the original work, add quotation marks with a citation to avoid plagiarism. This in-text citation must have the author’s last name with the year of publication and page number (preceded by “p.” or “pp.”). If you are directly quoting more than 40 words or longer, you would need to start the quotation on a new paragraph with a specified margin.
When you need to use a piece of copyrighted work in your study, it’s advisable to get permission from the copyright holder. In such a case, a written permission or an e-mail indicating the proof of permission is preferable.
Self-plagiarism is one of the most common types of plagiarism. Self-plagiarism is the publication of an author’s previous article as if it was a newly published work. In such cases, authors commonly re-use their own previous studies, images, or photos.
When you quote or paraphrase a text, temporarily highlight it to remind yourself that you need to add the proper citations later.
If you do not want to add your citations at a later time, you can use Microsoft Word Reference Module or another tool to add your citations and create your reference list automatically. By doing this, you don’t have to check whether you’ve cited all your sources appropriately, both in the in-text citations and the bibliography list.
Saving your sources gives you the opportunity to keep track of them. You don’t necessarily need a flawless list of citations formatted from the beginning.
A plagiarism check is the process of detecting instances of plagiarism within a document. The widespread use of computers and the advent of the Internet have made it easier to plagiarize the work of others. The detection of plagiarism can be undertaken in a variety of ways. There are several tools to run a plagiarism check. Find one and check your paper for a similarity report. When you upload your paper, the engine will examine the content and generate a similarity report, including the percentage of uniqueness of your text. Any copied words and expressions will be highlighted, and a list of sources with the same content will be presented.
Best Edit & Proof expert editors aim to provide your manuscripts with proper scholarly and academic tone and style. They will significantly improve the chances of having your research manuscript accepted for publishing. They provide subject-area proofreading and editing services in several fields categorized under various disciplines. With our extensive knowledge and expertise, we will help you find the right tone and style for your manuscript.
If you need our subject-area editors to format your manuscripts, giving you the fundamental rules for formatting your manuscripts as described in your guidelines, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles, then contact us. At Best Edit & Proof, our proofreaders and editors edit every type of academic paper. We have a user-friendly website, and a simplified ordering process.
If you would like our subject-area editors and language experts to work on your project for the improvement of its academic tone and style, then please visit the order page. It is easy! It takes only a few minutes to submit your paper and complete the process. Click here to see how it works.
We have flat-rate pricing based on our type of service (editing or proofreading), word count, and turnaround time. Enter your word count or copy and paste your document into our pricing calculator to get an instant quote.
If you need support for editing and proofreading services, contact us. You can also e-mail us or use the 24/7 live chat module to get direct support. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript. Alternatively, you can text us through our WhatsApp business line.
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium.
For more posts, click here.

For more information about the citation styles and APA style, read the following articles:
The 9 Most Important Changes in the 7th Edition of the APA Manual
How to Present Tables and Figures in APA Style (7th edition)
How to Cite Sources in APA Referencing Style? | With APA 7th Edition Update
This blog discusses the APA formatting guide for academic manuscripts. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
How to Cite Sources in APA Referencing Style | With APA 7th Edition Update
30.11.2020
Importance of Citations in Academic Writing
05.03.2022
How to Use Track-Changes Feature in Microsoft Word 2021
19.11.2020
How to Use ‘‘et al.’’ in APA Style (7th Edition)
28.11.2020
A Complete Guide to MLA In-Text Citations
01.06.2021
MLA Paper Format: How to Format a Paper in MLA Style
31.05.2021
How to Format DOI in APA Style (APA 7th Edition Update)
29.11.2020

When you are writing for academic purposes, you need to keep a ton of rules and regulations in mind. However, that is not the whole story, as you also need to keep the style guide in mind. While writing for academic work is not easy, nothing can be impossible with practice. Therefore, we are here with a compact citation style guide that abides by academic standards. If you are new to editing and proofreading or new to the academic side, this article will help you learn about the 8 most common citation styles used in academic writing.
Continue Reading
Turning on Track Changes function of your Microsoft Word document gives you an option to make changes that are easy to follow. The changes and revisions are like suggestions that one can review, and then remove by rejecting them or make them permanent by accepting them. This handout discusses how to show revisions inline or balloons in Tracked Changes.
Continue Reading
This reference guide explains how to format your academic documents in Microsoft Word 2022, giving you the fundamental rules for formatting your academic papers as described in most guidelines, such as MLA and APA styles. The rules discussed in this guide apply to most of the academic papers you will submit as college assignments or articles for journals.
Continue Reading
The American Psychological Association (APA) introduced the 7th edition of the APA Publication Manual (in October 2019), which replaces the 6th edition of the manual published in 2009. Since then, several things have changed. This article discusses the 9 most important changes in the 7th edition of the APA manual.
Continue Reading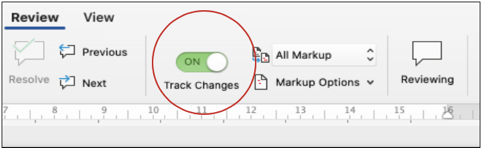
Track changes function in Microsoft Word 2021 for macOS is a very handy tool to track your revisions, corrections, changes, edits, and even suggestions and comments while you’re reviewing a document. When an editor or proofreader wants to return a revised document to a client with his/her all revisions visibly marked, and so clients can accept or reject, or the suggested changes appear in the margins of the returned document, he/she needs Track Changes function of Microsoft Word.
Continue Reading